
No more than code.
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。
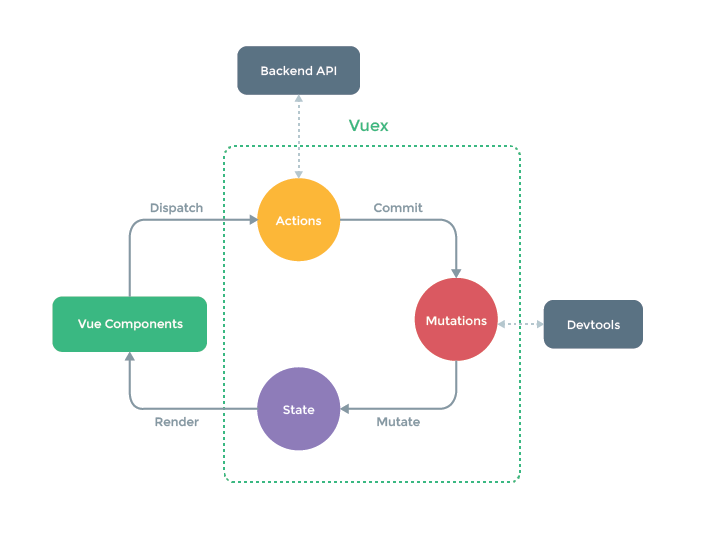
整体思路: 1、store.dispatch 分发action;(异步请求,需要action) 2、action进行异步处理,通过context.commit,提交给一个mutation 3、mutations 接收到action的commit,改变state 4、组件通过计算属性computed,获取仓库里面的数据
Vuex 和单纯的全局对象 不同:
- Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
- 改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交(commit) mutations[方便跟踪每一个状态的变化]。
Core Concepts : state、getters、mutations、actions、modules
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from "vuex";
// import VueResource from 'vue-resource';
Vue.use(Vuex);
// Vue.use(VueResource);
// 若请求数据 Vue.http.post
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:{
params:{}
},
getters:{
params(state){
return state.params;
}
},
mutations:{
search(state, data){
state.params = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data));
}
},
actions:{
search({commit},params){ // 筛选项
commit('search',params);
}
}
});
组件中获取 Vuex 状态的方法:在计算属性中返回。每当 store.state.count 变化的时候, 都会重新求取计算属性,并且触发更新相关联的 DOM。
// 创建一个 Counter 组件
const Counter = {
template: `<div>8</div>`,
computed: {
count () {
return store.state.count
}
}
}
mapState 辅助函数
当获取多个状态时,都声明为计算属性会重复和冗余。为解决此问题,可以使用 mapState 辅助函数生成计算属性:
// 在单独构建的版本中辅助函数为 Vuex.mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
}
接收两个参数:state 、其他 Getters
getters: {
// ...
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
我们可以很容易地在任何组件中使用它:
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount
}
}
mapGetters 辅助函数
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
如果你想将一个 getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式:
mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
Commit with Payload
store.commit 传入的额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload);
mutations: {
increment (state, n) {
state.count += n
}
}
store.commit('increment', 10)
通常情况下,payload 为一个对象,可以记录多个字段,更易读。
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
Object-Style Commit
另一种 commit a mutation 方法是使用包含 type 属性的对象
store.commit({
type: 'increment',
amount: 10
})
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
在组件中提交 Mutation
你可以在组件中使用 this.$store.commit(‘xxx’) 提交 mutation,或者使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
actions: {
increment (context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
}
Actions 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发,接收两个参数:
当需要 commit 多次时,可使用 ES2015 参数解构:
actions: {
increment ({ commit }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
Actions 支持 载荷方式 和 对象方式 进行分发
// dispatch with a payload
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10
})
// dispatch with an object
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10
})
this.$store.dispatch(‘xxx’), or use the mapActions helper
使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用:
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // map `this.increment()` to `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` also supports payloads:
'incrementBy' // map `this.incrementBy(amount)` to `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // map `this.add()` to `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
组合 Actions
store.dispatch 可以处理被触发的 action 的处理函数返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍旧返回 Promise
actions: {
actionA ({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('someMutation')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
}
// Now you can do:
store.dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
// ...
})
// And also in another action:
actions: {
// ...
actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
return dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
commit('someOtherMutation')
})
}
}
make use of async / await
// assuming `getData()` and `getOtherData()` return Promises
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // wait for `actionA` to finish
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}